NTU教授Hung-yi Lee 老师22年的机器学习网课笔记,学习!!
Introduction of Machine Learning
Machine Learning = Looking for Function
Different Types of Functions
- Regression (回归):The function outputs a scalar value.
- Classification (分类):The function outputs a class labeld.
How to Find the Function
Function with UnKnown Parameters(参数)
$y=f(x)$
$y=w*x+b$
$y=w_1 x_1+w_2 x_2+…+w_n x_n+b$
Define Loss from Training Data.误差函数是自己定义的,也可能是负数。
Loss is a function of parameters.
Loss: how good a set of value is.
Label: the true value.
$L=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n}(e_n)$
e=$abs(y_{true}-y_{pred})$ L is mean absolute error(MAE) 标准差
e=$\frac{1}{2}(y_{true}-y_{pred})^2$ L is mean squared error(MSE) 均方差
Error Surface: the surface of the loss function.根据参数的不同,loss的值不同,可以画出一个三维的图像,这个图像就是error surface
Minimize Loss by Optimizing Parameters.通过不断的调整参数,使得loss最小化
Gradient Descent(梯度下降法): a method to minimize the loss function.
hyperparameters: 人为设定的参数,比如learning rate, number of iterations.学习率和迭代次数
$\alpha$ : learning rate
$w_{new}=w_{old}-\alpha\frac{\partial L}{\partial w}$
$\frac{\partial L}{\partial w}$: the gradient of the loss function.
Repeat the process until convergence.
Linear Model 线性模型
Model Bias (模型偏差): 对于不同的数据集,模型的预测值和真实值之间的差距。
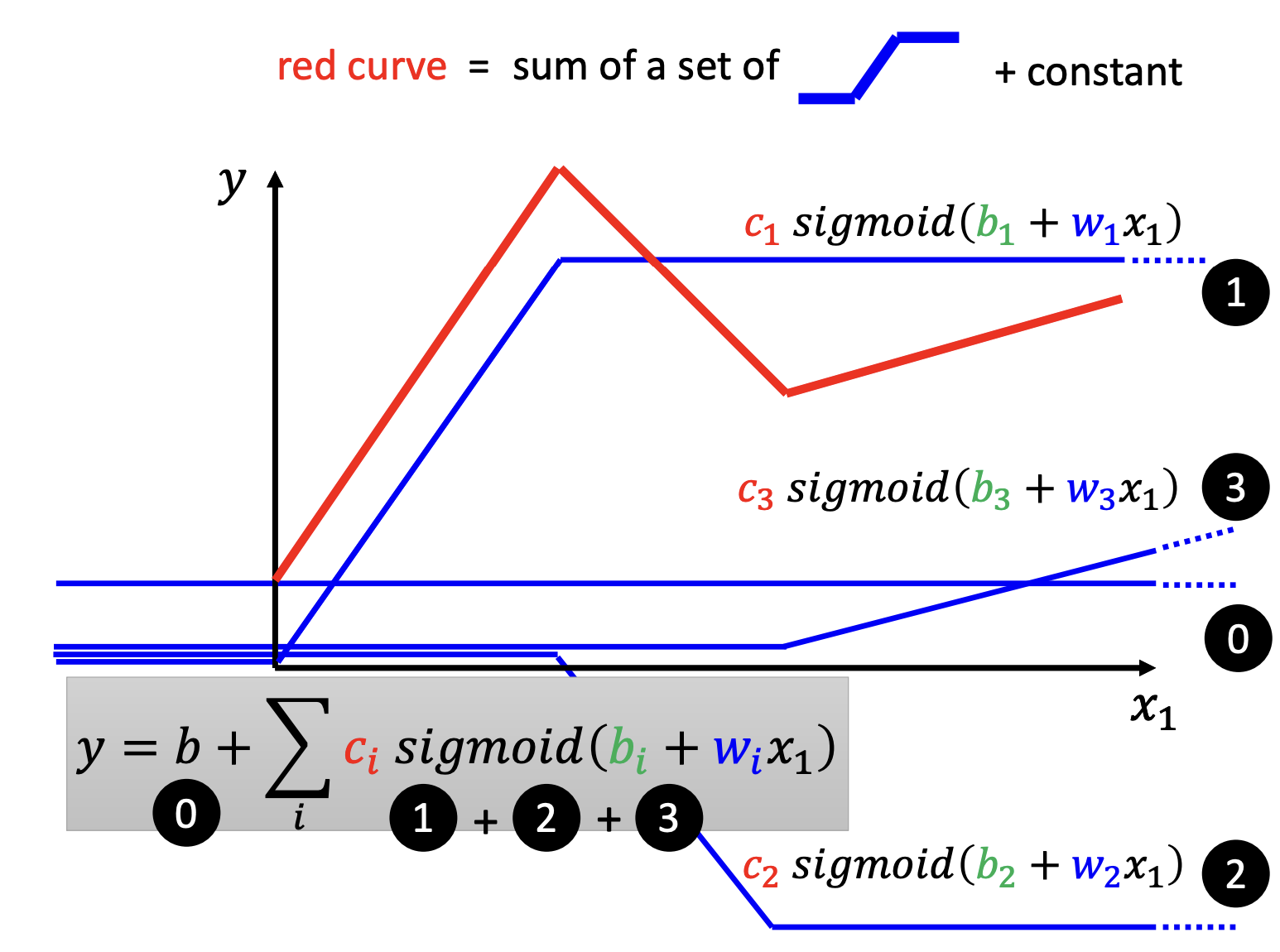
Piecewise Linear Model (分段线性模型): 通过多个线性模型的组合,可以拟合非线性的数据。
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
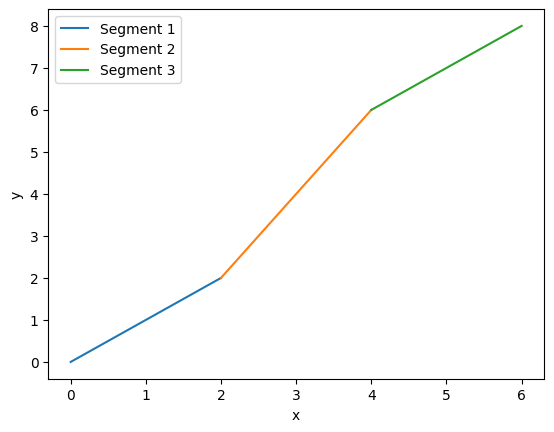
对于任何曲线,都可以用分段线性模型来拟合。
通过选取不同的函数类型,也可以更好地拟合数据。
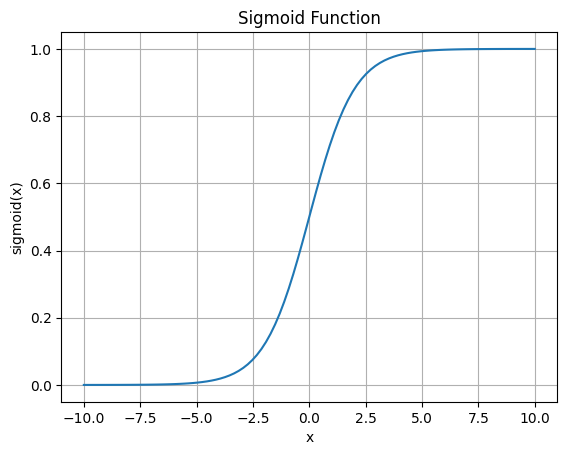
eg.对于z字型的曲线,可以使用soft sigmoid函数来拟合。
Soft sigmoid
- sigmoid function: $f(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-(b+wx_1)}}$
1 | import numpy as np |
对于一个分段曲线,就可以这样拟合:
ReLU
Rectified Linear Unit(ReLU)线性整流函数:
$ c\ max(0,b+wx_1)$
1 | import numpy as np |
Sigmoid 和 ReLU都可以叫做Activation Function激活函数,当然也有其他激活函数
Optimization of New Model
对于每一个未知的参数,用$\theta$来表示,将所有的参数放在一个向量中,用 $\mathbf{\theta}$ 来表示。
$$
\mathbf{\theta} = \begin{bmatrix}
\theta _0 \\
\theta _1 \\
\theta _2 \\
\dots
\end{bmatrix}
$$
目标是求出使L最小的$\mathbf{\theta}$
$\mathbf{\theta}^* = argmin _\mathbf{\theta}\ L(\mathbf{\theta})$
(Randomly) pick initial values for $\mathbf{\theta} _0$.
Compute gradient
$$
\begin{aligned}
& g=\nabla L(\mathbf{\theta}^0) \\
& \mathbf{\theta}^1=\mathbf{\theta}^0-\alpha g
\end{aligned}
$$Compute gradient
$$
\begin{aligned}
& g=\nabla L(\mathbf{\theta}^1) \\
& \mathbf{\theta}^2=\mathbf{\theta}^1-\alpha g
\end{aligned}
$$Repeat until convergence.
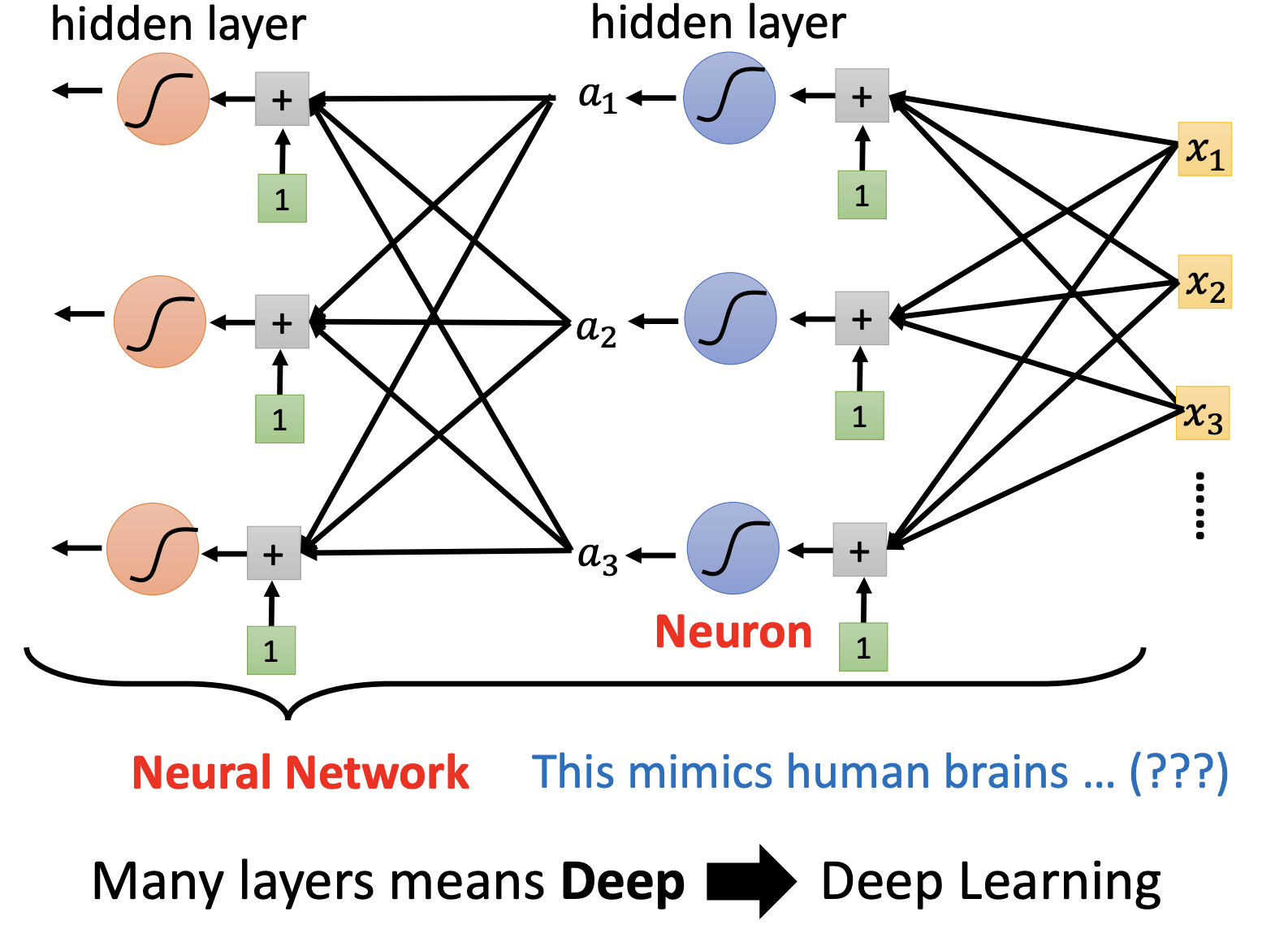
update、epoch、layer
batch :每次训练的数据量,相当于一个个包。
根据batch1,更新参数1,根据batch2,更新参数2,直到所有的数据都被训练过一遍。每一次更新所有参数,叫做一次update,所有的数据都被训练过一遍,叫做一个epoch。
通过一次激活函数我们可以得到$\mathbf{a}=\sigma(\mathbf{b}+w\mathbf{x})$,我们将a视为下一个变量x’,进行下一次利用激活函数求出$\mathbf{a’}=\sigma(\mathbf{b’}+w\mathbf{x’})$,像这样子一次运算求得的一个参数就叫做一个Neuron(神经元),每一排Neuron就叫做一个Later,所有Layer就是一个Neuron Network.




